The fuzzy ß-domain of MEF2D, NMR and computational studies
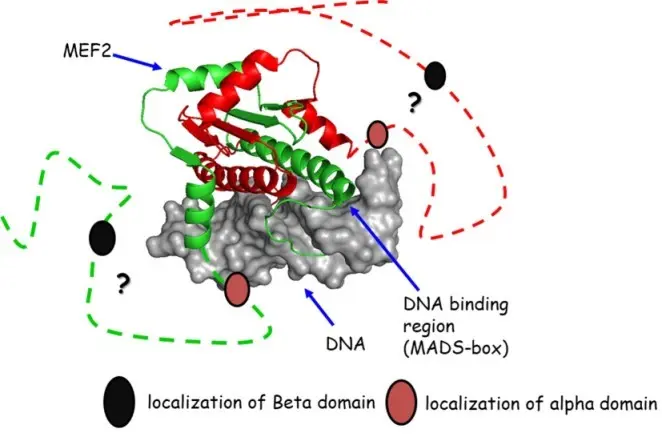 The MEF2 transcription factors play crucial roles in muscle cell myogenesis and morphogenesis. Bioinformatical analysis indicates that the alternatively spliced β-domain of MEF2D does not fold into a well-defined structure and also remains to be conformationally heterogeneous upon interactions. To study the role of protein dynamics in the biological function, a series of dynamical variants, 15-37 AA model peptides were designed. Detailed analysis of the dynamical and structural properties of the peptides (relaxation, diffusion, secondary chemical shifts and in silico MD-calculations) will give insights into the altered interaction patterns of the MEF2D β-domain corresponding to altered biological activities.
The MEF2 transcription factors play crucial roles in muscle cell myogenesis and morphogenesis. Bioinformatical analysis indicates that the alternatively spliced β-domain of MEF2D does not fold into a well-defined structure and also remains to be conformationally heterogeneous upon interactions. To study the role of protein dynamics in the biological function, a series of dynamical variants, 15-37 AA model peptides were designed. Detailed analysis of the dynamical and structural properties of the peptides (relaxation, diffusion, secondary chemical shifts and in silico MD-calculations) will give insights into the altered interaction patterns of the MEF2D β-domain corresponding to altered biological activities.
Left: The MEF2A-DNS complex (NMR-structure) (PDB: 1C7U)
Structural studies of UV-sensitive cyclic peptides
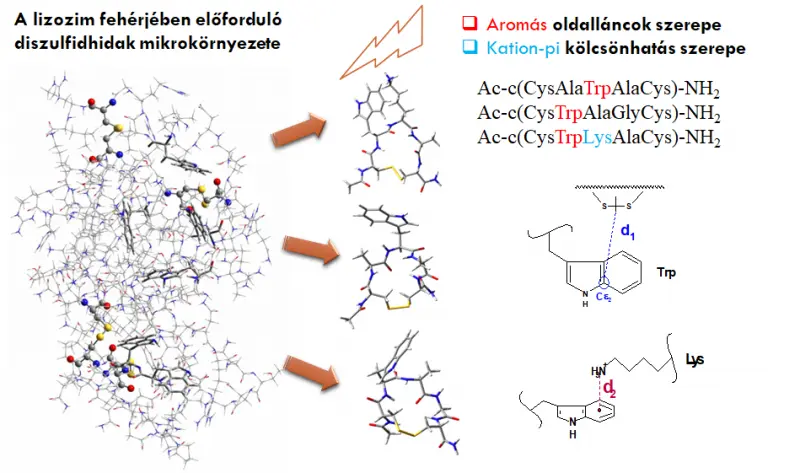 Disulfide bridges in enzymes are responsible for stabilizing the biologically active structure of proteins. The activity or role of a protein in a living organism can be modified or even destroyed by UV-light mediated photolysis. The chemical environment of the disulfide bridges (aromatic side chains, cromophores, stabilizing effects, dynamics) strongly affects the mechanism of the possible photolytic processes, which is studied by in collaboration with Dr. Zsuzsa Majer. Conformational and dynamical properties of peptide models cyclized via disulfide bonds are being investigated by molecular simulations (MD) and NMR.
Disulfide bridges in enzymes are responsible for stabilizing the biologically active structure of proteins. The activity or role of a protein in a living organism can be modified or even destroyed by UV-light mediated photolysis. The chemical environment of the disulfide bridges (aromatic side chains, cromophores, stabilizing effects, dynamics) strongly affects the mechanism of the possible photolytic processes, which is studied by in collaboration with Dr. Zsuzsa Majer. Conformational and dynamical properties of peptide models cyclized via disulfide bonds are being investigated by molecular simulations (MD) and NMR.